LN2535 based low-cost mobile phone charger application
- CC/CV (constant current / constant voltage) 5V/1A
1. brief introduction
This is a low cost mobile phone charger based on LN2535 design program report. This scheme uses LN2535 to drive an external NPN transistor, such as 13003, which is a typical low cost switching power supply scheme. This scheme has the characteristics of low cost, no optocoupler and Y capacitor, good constant current / constant voltage performance and low standby power dissipation. This application is especially suitable for small power charger where cost control is sensitive, such as cell phone charger, charger for MP3 player, etc.. The contents of this paper include circuit schematics, material list, transformer files and performance test data.
Program basic characteristics:
- Ultra low cost mobile phone charger controlled by PWM
- Primary adjustment technique
- Non optical coupler
- No Y capacitor and common mode EMI filter are required
- 85VAC-264VAC full voltage input range
- Low standby power
- High precision constant current and constant voltage output
- Exceed the CEC average efficiency requirements
- Less external components
- Integrated input voltage change compensation circuit
- Inductance change compensation circuit of integrated transformer
- Integrated output line loss compensation circuit
- Input undervoltage protection, input overvoltage protection
- Output short circuit protection and output overvoltage protection
- Over temperature protection
- Flyback DCM operating mode
- SOT23-5 packaging
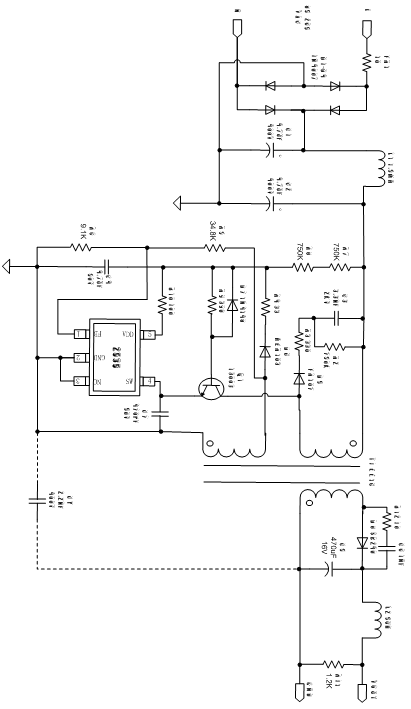
2.The circuit principle diagram
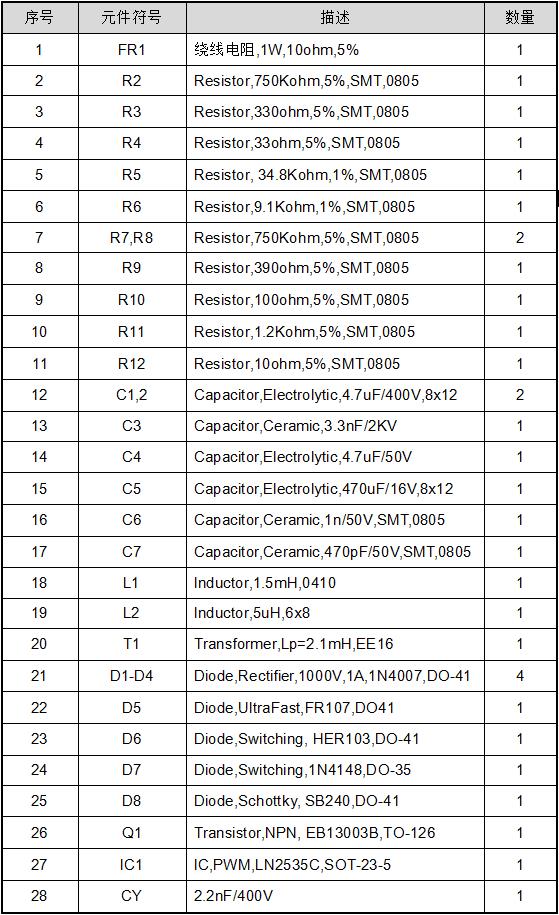
3. Bill of materials
4. Transformer specification
4.1. Sketch Map
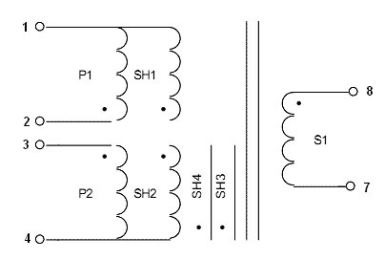
Schematic diagram of transformer
4.2. Bill of materials
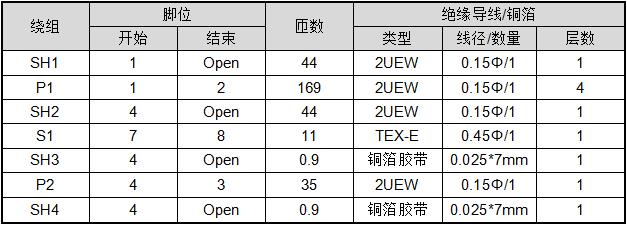
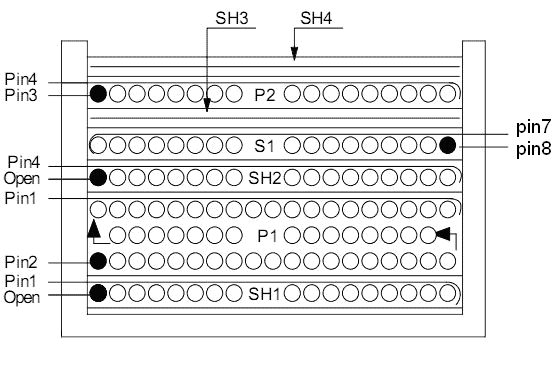
Note: SH1 and SH2 are shielding layers, SH3 and SH4 are copper foil shielding layers, P1 and P2 are primary, and S1 is secondary.
4.3 assembly drawing
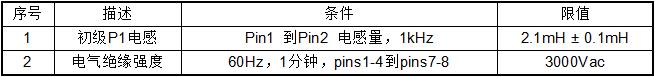
4.4. Electrical specification
5. Performance test data
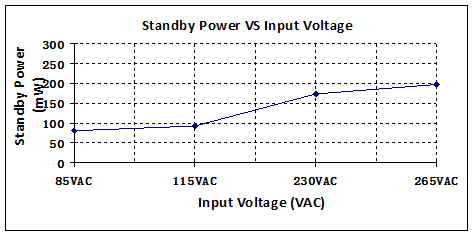
5.1. standby power

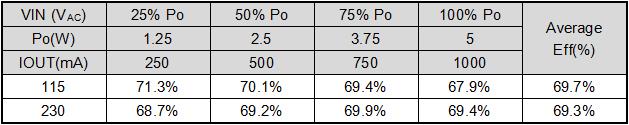
5.2. efficiency(AWG24#,1.5m)
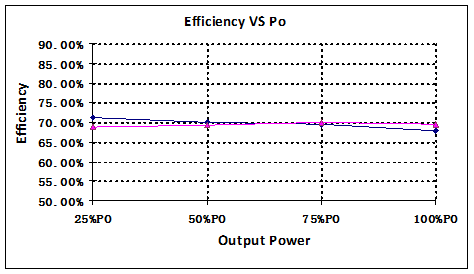
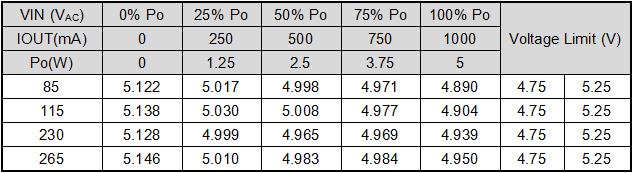
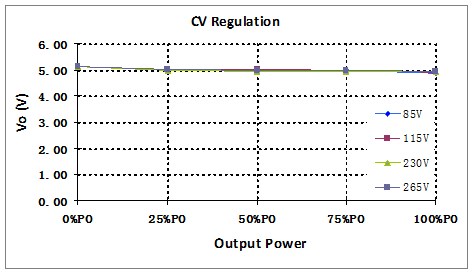
5.3. Input voltage and load regulation
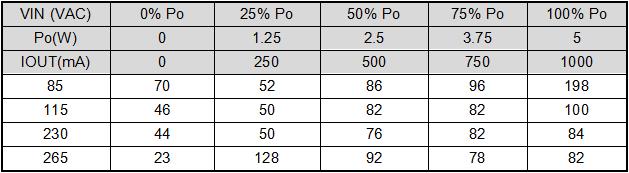
5.4. Ripple and noise
5.5. Power on and off
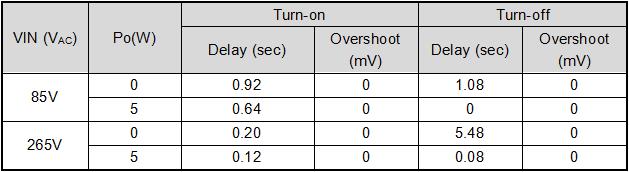
5.6. Constant current and overcurrent
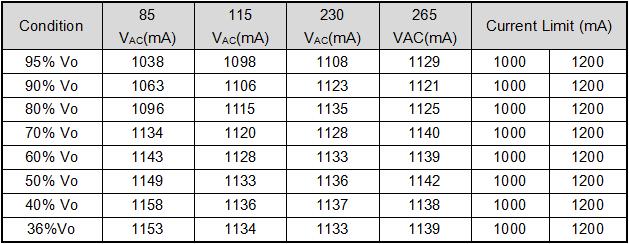
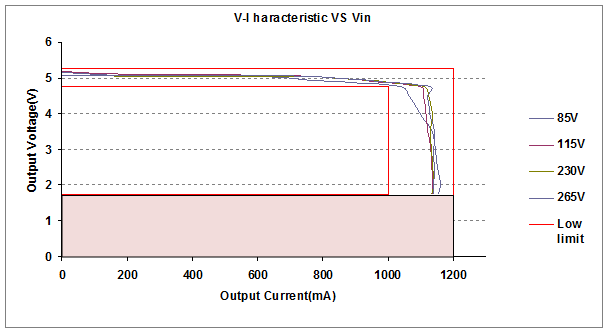
5.7. Short circuit and release

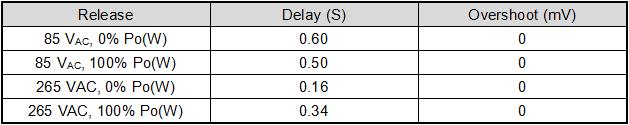
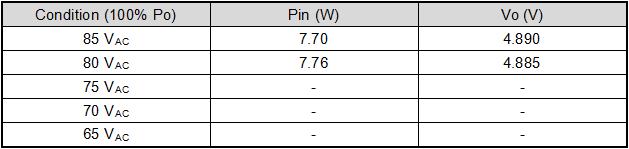
5.8. Input undervoltage test
6. Withstand voltage test;
6.1 withstand voltage test







 Wechat
Wechat